Improving volatile fatty acid yield from sludge anaerobic fermentation through self-forming dynamic membrane separation.
Hongbo Liu, Bo Yin, Yanfang Zhu, Bo Fu, He Liu. 全文下载
School of Environmental and Civil Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu Province, PR China
Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment, Suzhou 215011, China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Anaerobic Biotechnology, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu Province, PR China
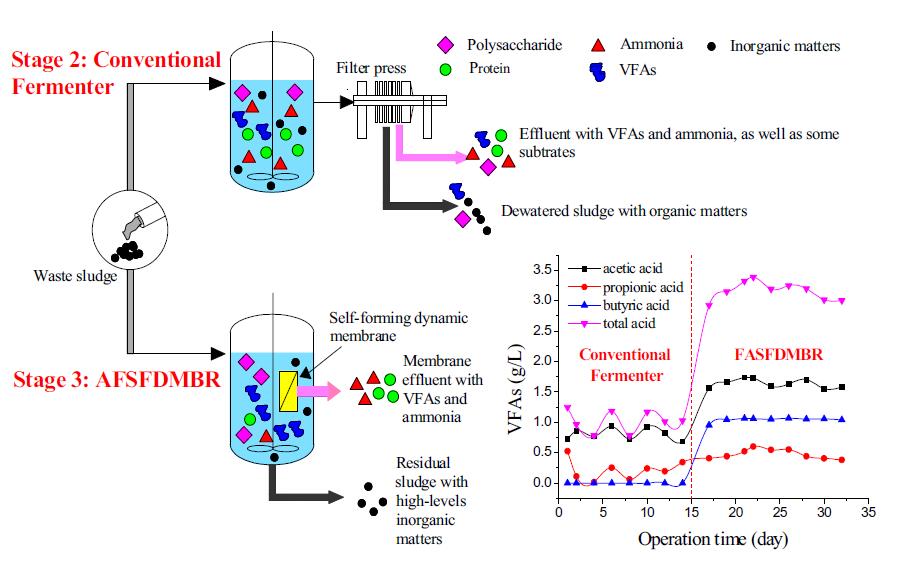
Self-forming dynamic membrane (SFDM) separation was applied to the conventional sludge fermenter for improving VFA yields. Results indicated SFDM presented good performance in transferring products, retaining substrates, and enriching useful bacteria. The retention ratios of suspended solids, soluble COD, proteins, and polysaccharides reached 99%, 30%, 70%, and 40%, respectively, and more than 90% of the VFAs and ammonia could be transferred in a timely manner. The structure of the microbial community was optimized, which led to enhanced releases of hydrolytic enzymes and accelerated enrichments of functional bacteria. Protease and β-glucosidase activities increased from 1.0 to 5.0 U/mL and 15.0 to 23.0 μmol/L·h, respectively. VFA yield and sludge conversion ratio increased by 233.3% and 227.9%, respectively. Moreover, SFDM had good operation stability, including a short formation time, a long operation period, and a low transmembrane pressure. These results show VFA yield from sludge fermentation can be greatly improved by SFDM separation.
Anaerobic fermentation; Self-forming dynamic membrane; Separation; Sludge; Volatile fatty acids;
Bioresource Technology
Elsevierjournal
10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.077
2016
92-100
Elsevier Ltd
