Silicate mediated simultaneous in-situ CO2 sequestration and nutrients removal in anaerobic digestion.
He Liu, Linlin Gong, Yan Zhang, Qianqian Jiang, Minhua Cui, Jie Zhang, Bo Fu, Hongbo Liu 全文下载
School of Environment and Civil Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Anaerobic Biotechnology, Wuxi 214122, China
Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Water Treatment Technology and Material, Suzhou 215011, China
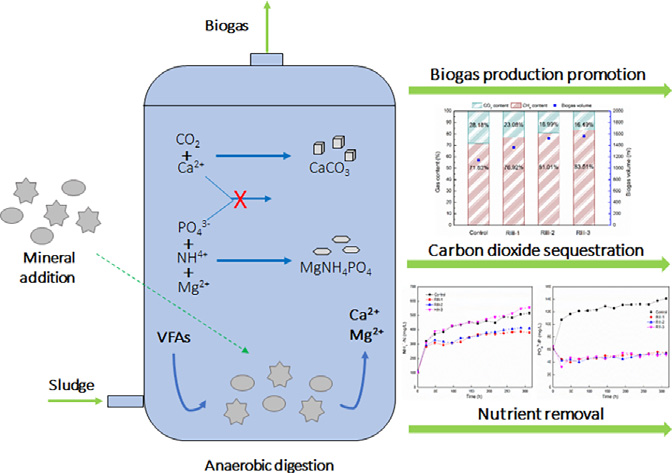
This study investigated the reactions among CO32− , PO43−, NH4+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, under different CO32− concentration and Mg2+/Ca2+ ratio, and conducted sludge anaerobic digestion (AD) with silicate addition to achieve in-situ CO2 sequestration and nutrients removal. High CO32− concentration facilitated the formation of MgNH4PO4, and Mg2+/Ca2+ ratio of 1:1 achieved best CO32−, PO43−, and NH4+ removal in simulated anaerobic digestate. Supplementation of 40 g/L magnesium silicate combined with 20 g/L wollastonite decreased CO2 content in biogas from 28.2% to 19.0%, and removed PO43− and NH4+ by 61.8% and 21.2%, respectively, in AD. Simultaneous in-situ CO2 sequestration and nutrients removal was achieved by directed precipitation of PO43− , NH4+ , and CO2 with silicate released Mg2+ and Ca2+, to form MgNH4PO4 and CaCO3. Meanwhile, methane production was improved by 51.2% with silicate supplementation. This study provides an attractive measure for CO2 and nutrients removal as well as methane production enhancement of sludge AD.
Anaerobic digestion; Mineral carbonation; CO2 sequestration; Nutrients removal; Silicates;
Bioresource Technology
Elsevierjournal
10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.004
2019
125-132
Elsevier Ltd
