Mass transfer intensification in a novel airlift reactor assembly with helical sieve plates.
Zhiyong Zheng, Yuqi Chen, Xiaobei Zhan, Minjie Gao, Zifan Wang 全文下载
Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology of Ministry of Education, School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Anaerobic Biotechnology, School of Environment and Civil Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
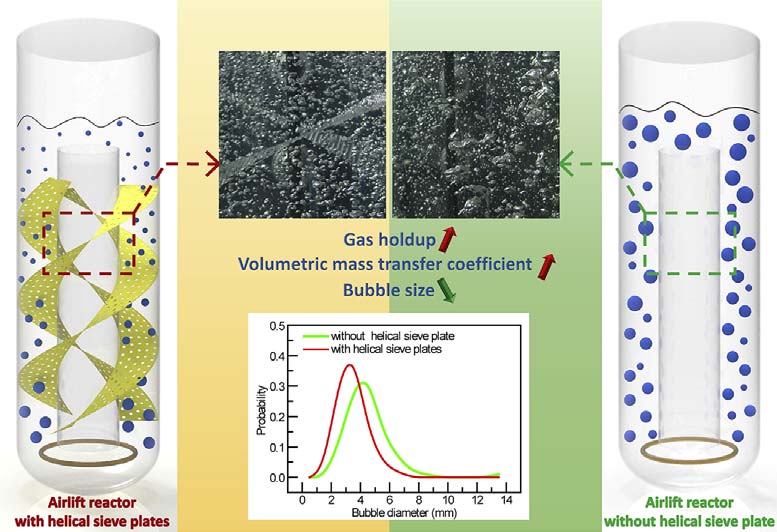
A novel airlift reactor (ALR) assembly with helical sieve plates (HSPs) in the riser section was developed to intensify gas–liquid mass transfer process. The mass transfer and mixing characterization of the ALR assembly with different HSP structures was analyzed and compared using gas holdup, volumetric mass transfer coefficient, bubble velocity, and mixing time as assessment parameters. With optimized HSP, the gas holdup and volumetric mass transfer coefficient of the reactor were significantly increased by 38–53% and 76–144%, respectively, compared with those of the classical ALR. The empirical equations of gas holdup and volumetric mass transfer coefficient in the new ALR under the experimental condition were proposed. With the increase in the free area ratio in the HSP, a large numberof bubbles were broken into small bubbles. Thereafter, the gas–liquid mass transfer efficiency was improved by increasing the gas–liquid interfacial area. Large helix angle caused part of the bubbles to flow helically. As a result, the circumferential mixing of fluid was enhanced whereas the overall mixing time was shortened.
Bioreactor; Gas holdup; Mixing; Bubble sizes; Bubble breakup
Chemical Engineering Journal
Elsevierjournal
10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.039
2018
61-70
Elsevier B.V.
